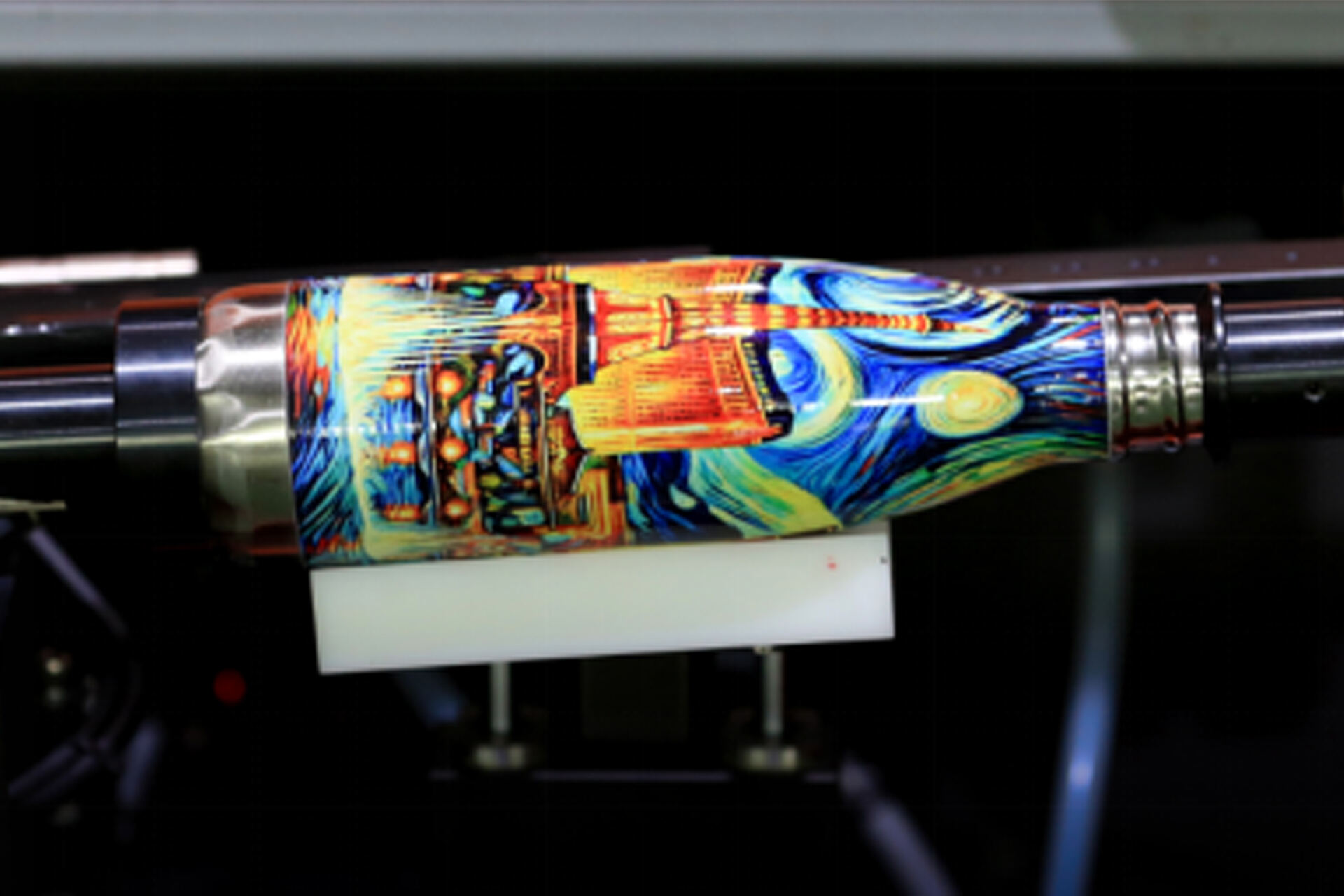

Digital printing is a revolutionary way of reproducing images and text onto various surfaces. It’s fast, accurate, and produces high-quality prints without the need for traditional printing plates or screens. This has revolutionized the printing industry, making it more efficient and accessible. Images are directly transferred from a computer to the substrate using inkjet technology. No time-consuming setup processes, such as plate-making or screen preparation. That makes it great for small to medium print runs. It also offers flexibility in customization and personalization. Complex designs and gradients are reproduced accurately with digital printing. This is due to advanced color management systems and precise inkjet technology.
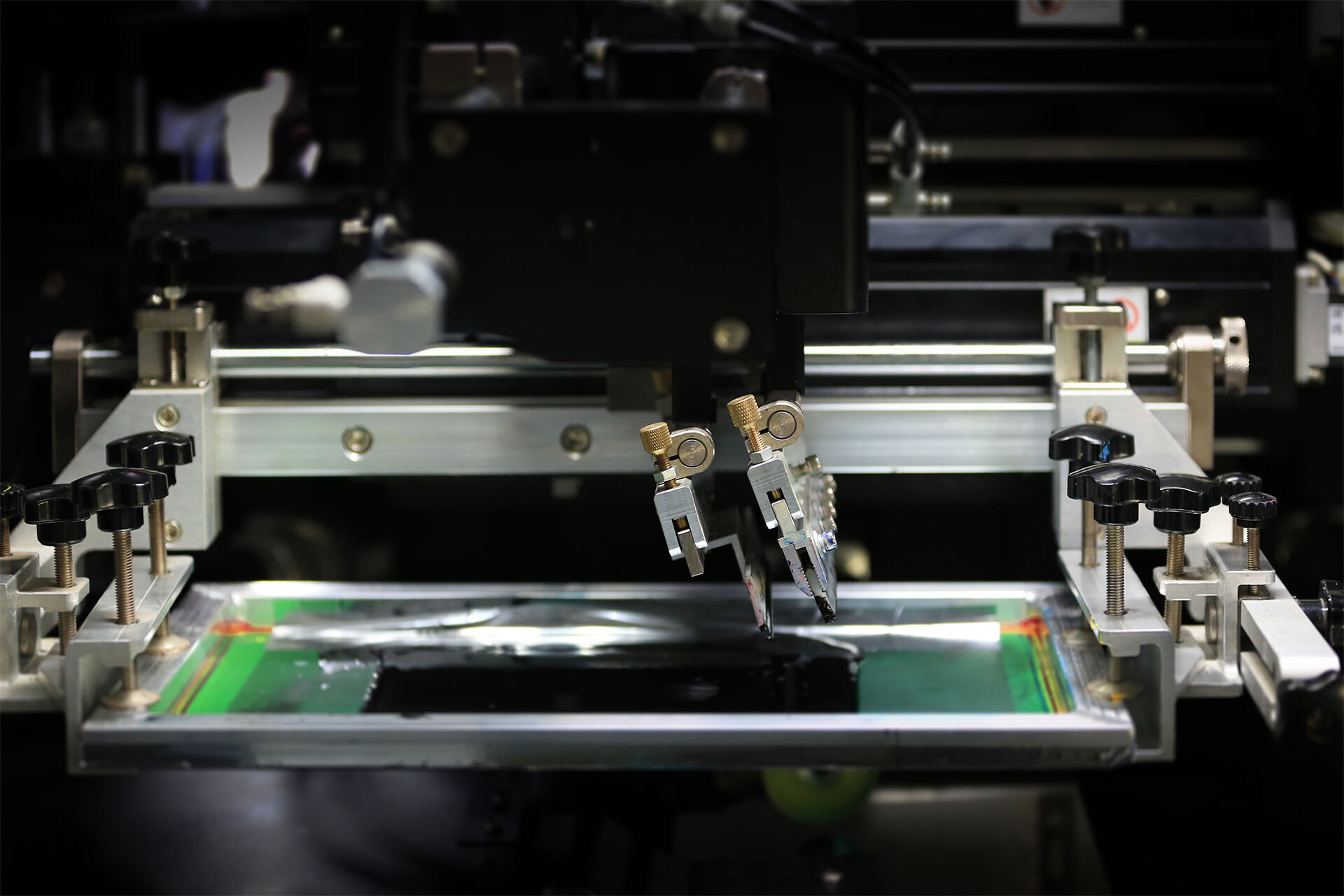

Screen printing is a technology, where the print material is pressed by a squeegee through a mesh that is fixed on a frame. The mesh carries a photoresist layer with openings defining the pattern to be printed. Our machines can print on various materials and shapes, such as glass, plastics, metal and ceramics. Cylindrical, oval and square.
The hot stamping process is a printing technique that applies a metallic foil onto a surface using heat and pressure. This technique is commonly used to create decorative accents or logos on various materials. For glass, need to screen print primer first, then stamping by silicone roller, the foil was transferred onto primer, not directly to glass. For plastic, begins by creating a die or mold of the desired design, which is usually made of brass or magnesium. The die is heated and pressed onto the material, transferring the foil onto the surface.
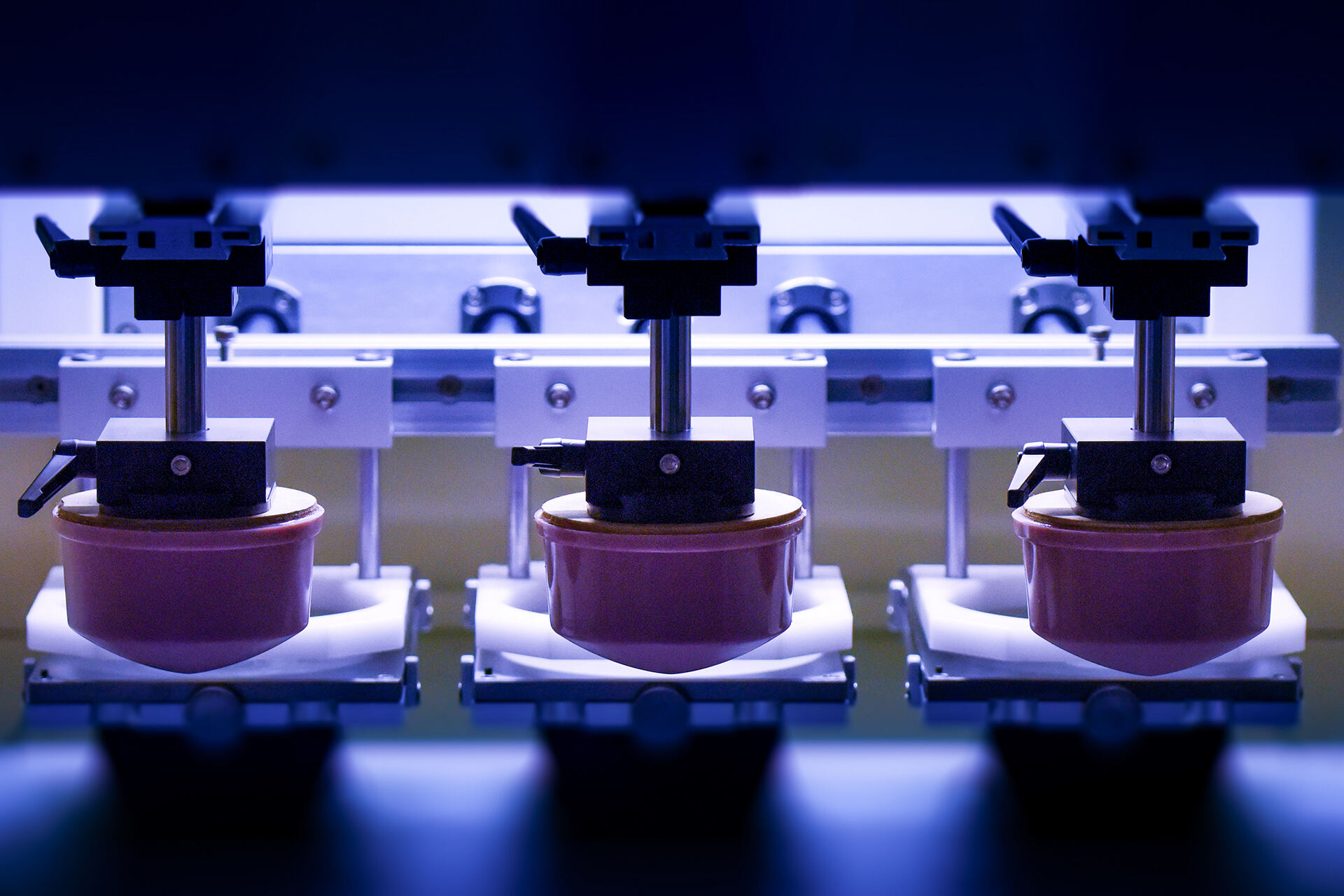

Pad printing, also called tampography or tampo printing, is a printing process that can transfer a 2-D image onto a 3-D object. This is accomplished using an indirect offset (gravure) printing process that involves an image being transferred from the cliché via a silicone pad onto a substrate. The unique properties of the silicone pad enable it to pick the image up from a flat plane and transfer it to a variety of surfaces, such as flat, cylindrical, spherical, compound angles, textures, concave, or convex surfaces.